What is Colostrum, It’s Benefits, and Why Your Baby Needs It
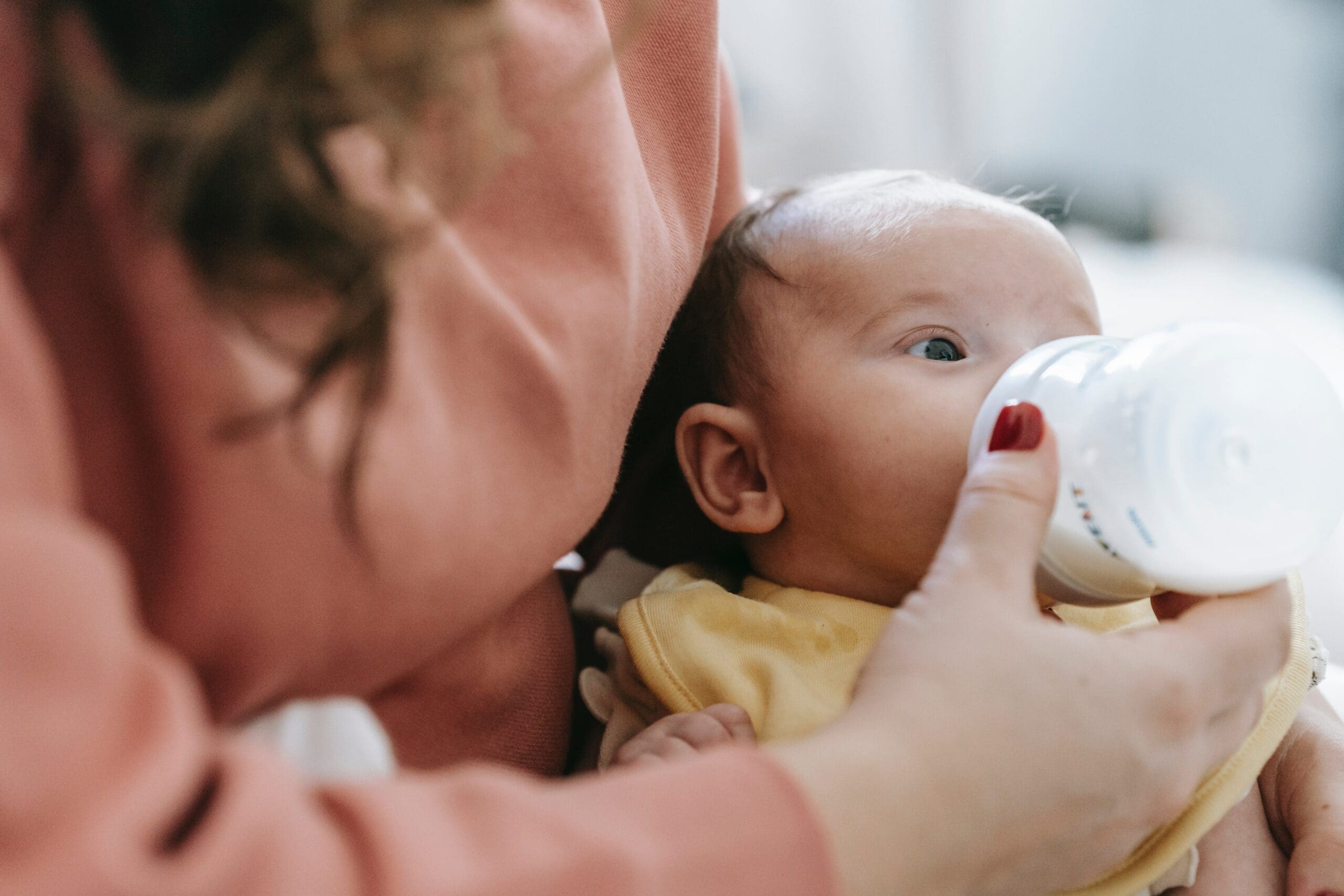

Colostrum, often referred to as “liquid gold,” is the first milk produced by a mother’s breasts in the initial days after childbirth. It is a thick, yellowish fluid packed with vital nutrients and antibodies that play a crucial role in the early development and health of newborns.
In this blog, we will explore what colostrum is, the benefits it provides to both babies and mothers and what to expect during this period.
What is Colostrum
Colostrum is a highly concentrated milk-like substance that is secreted by the breasts during the first few days after delivery. It is distinct from mature breast milk in terms of its composition and benefits.
Colostrum is rich in proteins, antibodies (including immunoglobulins such as IgA), epidermal growth factors, vitamins, minerals, and other bioactive compounds. These components provide essential nutrition and protection to the newborn.
What are the Differences Between Colostrum and Breast Milk?
Colostrum and breast milk differ significantly in several important ways:
- Immunoglobins, which are abundant in colostrum, help your baby’s immune system function better and keep it healthy.
- Protein content in colostrum is two times higher than breast milk.
- Zinc content in colostrum is four times higher than breast milk.
- Colostrum is simpler to digest because it contains less sugar and fat.
- Colostrum has a yellowish color and thicker consistency.
Benefits of Colostrum for Babies
- Nutrition: Colostrum is a rich source of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, and vitamins, which provide the newborn with vital nutrients for growth and development.
- Immune Support: Colostrum contains a high concentration of antibodies, which help strengthen the baby’s immune system, protecting them against various infections and diseases.
- Digestive Health: The proteins and growth factors present in colostrum support the development of the baby’s digestive system and aid in the passage of meconium (the baby’s first stool).
- Brain Development: Colostrum also contains important fatty acids like DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), which are essential for brain development and cognitive function.
- Allergy Protection: The antibodies in colostrum can help reduce the risk of allergies and intolerances in newborns.
Benefits of Colostrum for Mothers
- Uterine Contractions: The release of oxytocin triggered by breastfeeding colostrum helps the mother’s uterus contract, reducing postpartum bleeding and promoting a quicker return to pre-pregnancy size.
- Bonding and Emotional Well-being: Breastfeeding colostrum creates a special bond between the mother and the baby, releasing hormones that promote feelings of love, nurturing, and relaxation.
- Breast Health: Frequent breastfeeding during this period helps establish milk supply, prevents engorgement, and reduces the risk of breast complications such as mastitis.
- Weight Loss: Breastfeeding, including colostrum, can aid in postpartum weight loss by burning extra calories and helping the uterus return to its pre-pregnancy size.
What to Expect during the Colostrum Period
Quantity: Colostrum is produced in relatively small amounts, typically ranging from teaspoons to tablespoons per feeding. This is normal, as the baby’s stomach is tiny and requires small, frequent feedings.
Color and Consistency: Colostrum is usually yellowish or golden in color and has a thick, sticky consistency. It may also appear more concentrated than mature milk.
Frequency of Feeding: Newborns may feed more frequently during the colostrum period, often every 1-3 hours. This helps establish milk supply and ensures the baby receives sufficient colostrum.
Transition to Mature Milk: Over time, colostrum transitions into mature breast milk, which is thinner and whiter in appearance. This transition usually occurs within a few days after birth.
Colostrum FAQ
How long will a mother produce colostrum?
Mothers will typically produce colostrum for the first few days after delivery, usually up to around 5-7 days. Mothers can consider consuming nourishing and nutritious breakfast and snacks right after delivery and during confinement period to aid production of colostrum. There are three different stages of breast milk, the first one being colostrum, then you will have transitional milk and lastly, mature milk.
Can you store colostrum?
Yes, colostrum can be stored for future use. It is recommended to express and store colostrum in clean, sterile containers specifically designed for breast milk storage. Label the containers with the date and time of expression and store them in the refrigerator or freezer according to guidelines provided by healthcare professionals or lactation consultants.
How long can colostrum be stored?
Colostrum can be stored in the refrigerator for up to 48-72 hours. If you need to store it for a longer period, it can be kept in the freezer for up to 3-6 months. However, it is important to follow proper storage guidelines to maintain its quality and safety.
How often should a newborn be fed colostrum?
Newborns should be breastfed on demand, whenever they show signs of hunger. This can range from 8 to 12 or more feedings per day, including during the colostrum period. It is important to pay attention to the baby’s hunger cues and feed them whenever they are hungry, even if it means frequent feedings.
Is colostrum enough to meet a newborn’s nutritional needs?
Yes, colostrum is designed to meet a newborn’s nutritional needs during the initial days after birth. It is highly concentrated and provides the necessary nutrients and antibodies for the baby’s growth and development. The small amounts of colostrum produced are sufficient for the baby’s tiny stomach and serve as the perfect first food.
How does colostrum differ from mature breast milk?
Colostrum is produced in the first few days after birth and is rich in antibodies, proteins, and other immune-boosting components. It is thicker and yellower in color compared to mature breast milk. Mature breast milk, produced after the colostrum period, is thinner and whiter in appearance and contains a balanced mix of fats, proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals to support the baby’s ongoing nutritional needs.
Can colostrum be supplemented with formula?
While colostrum is highly beneficial for newborns, there may be situations where supplementation with formula is necessary or recommended. This is best discussed with healthcare professionals or lactation consultants, who can provide guidance and support based on individual circumstances.
Conclusion
Remember, every breastfeeding journey is unique, and it’s important to seek guidance from healthcare professionals, such as doctors or lactation consultants, for personalized advice and support regarding colostrum and newborn nutrition.