What are the benefits of breastfeeding premature babies?
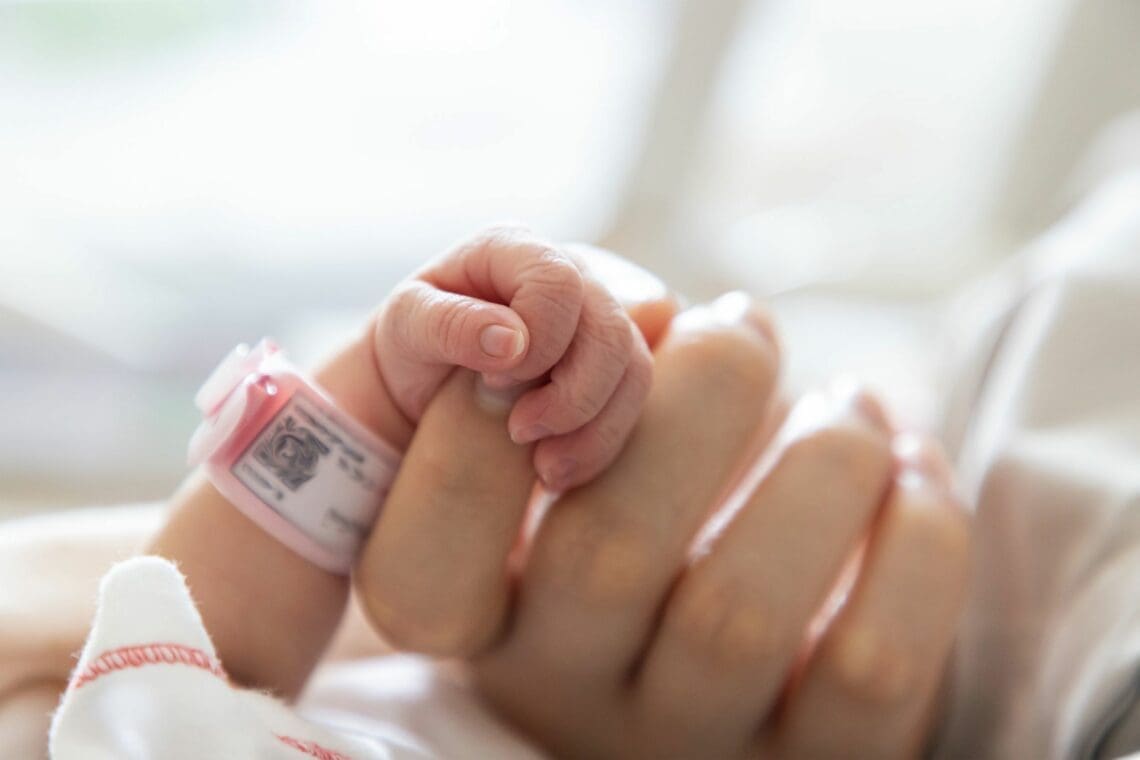

Premature or preterm birth is the term used to describe a child born before 37 weeks of gestation. Premature babies may require treatment in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) or special care baby unit (SCBU) for assistance with breathing, maintaining body temperature, preventing fluid loss, feeding, or other medical difficulties.
Breastfeeding is a natural and beneficial way to nourish a newborn baby. It provides the perfect balance of nutrients that an infant needs for healthy growth and development. There are numerous benefits to breastfeeding for both the baby and the mother. In this article, we will explore the benefits of breastfeeding, why it’s good for premature babies, how it affects infant development, and ways for mothers to improve their breast milk.
Why is it so important to feed your premature baby breast milk?
Premature babies are at a higher risk of developing several medical complications. These complications can be life-threatening and require specialized medical care. Breast milk is especially important for premature babies, as it provides the necessary nutrients for their growth and development.
As the digestive and immune systems of a premature baby are immature, breast milk is easier to digest and filled with antibodies that help protect them from infections. Breast milk also helps reduce the risk of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), a serious condition that affects the intestines of premature babies.
A study published in The Lancet found that breastfeeding could prevent over 800,000 child deaths globally each year. Boosting breastfeeding rates for infants below 6 months of age would cut treatment costs for common childhood illnesses such as pneumonia, diarrhea, and asthma and save healthcare systems billions of dollars.
Several studies have shown that premature babies who received mothers’ milk had better cognitive outcomes compared to those who did not receive mothers’ milk. The same studies have found that never‐breastfed children faced a higher risk of having suboptimal nonverbal and verbal cognition at 2 years of corrected age when compared with those who were breastfed.
Other studies have also found that breast milk contains several bioactive components that are important for infant growth and development, including growth factors, hormones, and immune cells. Breastfeeding can improve the overall health outcomes for premature babies.
Benefits of breastfeeding premature babies and newborns
Breastfeeding offers numerous health benefits for the baby, including:
- Optimal nutrition: Breast milk is the perfect food for newborns as it contains all the essential nutrients that a baby needs for growth and development. Breast milk provides the right balance of proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals that are easily digestible by a baby’s immature digestive system.
- Boosts immunity: Breast milk contains antibodies that help protect babies from infections and illnesses, especially in the first few months of life when the immune system is still developing.
- Reduced risk of SIDS: Breastfeeding has been shown to reduce the risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) by up to 50%.
- Cognitive development: Breastfed babies have been shown to have better cognitive development and higher IQ scores compared to formula-fed babies. According to the World Health Organization, breast milk helps the development of the brain and the nervous system.
- Reduced risk of chronic diseases: Breastfeeding has been associated with a reduced risk of chronic diseases such as obesity, diabetes, and asthma later in life.
When can I start breastfeeding my premature baby?
You can start breastfeeding your baby as early as 29 weeks of gestation. However, when a baby is premature, both the baby and the mother can face challenges since many of the reflexes required for breastfeeding, such as the rooting reflex, the ability to coordinate sucking, swallowing, and breathing, and the extension of the tongue to grasp the breast, may not be fully developed among premature babies.
However, it is critical to start trying to breastfeed your newborn, as breast milk is extremely beneficial for premature babies and newborns in general. Breastfeeding has been shown to have a positive impact on infant development. Breastfed babies have better cognitive and visual development than formula-fed babies. Breastfeeding also helps promote bonding between the mother and baby, which is important for emotional development.
How can mothers improve their breast milk?
Mothers can take several steps to improve the quality and quantity of their breast milk and achieve breastfeeding success:
Eat a healthy, balanced diet: Mothers should eat a healthy, balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, nuts, and lean protein. They should also drink plenty of water to stay hydrated. There are a good variety of tasty snacks that contain the lactogenic ingredients that mothers need.
Get enough rest: Getting enough rest is important for milk production. Mothers should aim to get at least 7-8 hours of sleep each night.
Breastfeed frequently: Breastfeeding frequently helps stimulate milk production and ensure that the baby gets enough milk.
Use breast pumps: Using a breast pump can help increase milk supply and also provide the baby with milk when the mother is away.
Seek support: Breastfeeding can be challenging, especially in the early days. Mothers should seek support from a lactation consultant or a breastfeeding support group.
Conclusion
In conclusion, breastfeeding offers numerous benefits for both the baby and the mother. Even if you have a premature baby, you should start to breastfeed your baby as soon as possible, as breast milk poses many benefits for premature babies.
Breast milk provides optimal nutrition, boosts immunity, and promotes cognitive development. Breastfeeding is especially important for premature babies as it helps reduce the risk of infections and NEC.
During the lactation journey, a mother’s body requires more energy and nutrients in order to produce milk and give the baby the nutrition it needs. It is possible to make sure that the mother’s body has all the nutrients required to boost milk production by eating a well-balanced diet composed of a variety of foods. In sum, mothers can improve the quality and quantity of their breast milk by eating a healthy diet, getting enough rest, breastfeeding frequently, using breast pumps, and seeking support.